In 1929, Edwin Hubble discover that the farther the galaxy is, the faster it is moving away from us, this is known as the Hubble law.
In the formula, v is the recession velocity measured in km/s,
is Hubble Constant, =68km/s/Mpc and d is the distance in Mpc. This provide us with a method to measure distance of extremely distant galaxies using redshift.Define redshift , a dimensionless quantity that indicates how much the wavelength of light has increase relative to the original wavelength.
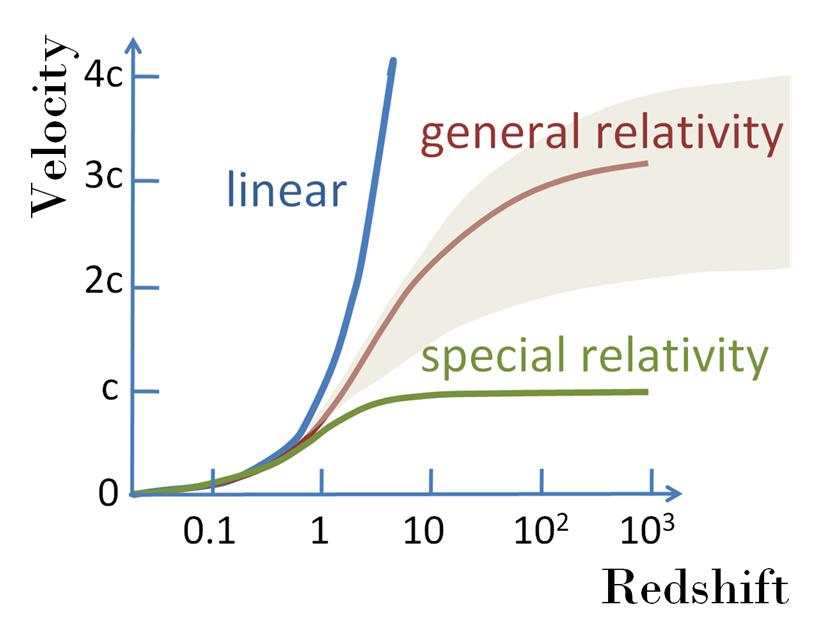
Note that the value of redshift can be both positive and negative. By Doppler effect , one can determine the relative velocity with the observer.
Let's first analyze the equation:
Before you jump in and use this law, there are some things you should know in advance:
